Legacy and Boeing 727 History
The Boeing 727 first took to the skies on February 9, 1963, marking the start of a new era in jet airliner development. As part of the wave of early jets that reshaped air travel, the 727 stood out for its versatility and innovation. Designed to serve both major airports and smaller regional hubs, it offered unmatched flexibility with its efficient tri-jet configuration and ability to operate on shorter runways—qualities that quickly made it a game-changer for commercial aviation.
Shortly after its introduction, the Federal Aviation Administration granted certification, allowing airlines to begin widespread operations. United Airlines was among the first major carriers to put the Boeing 727 into service, solidifying its role as a reliable workhorse in the skies.
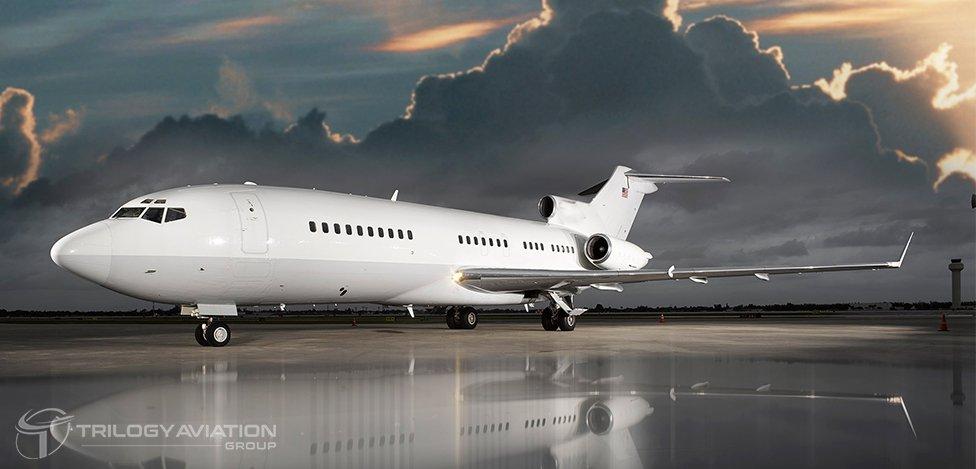
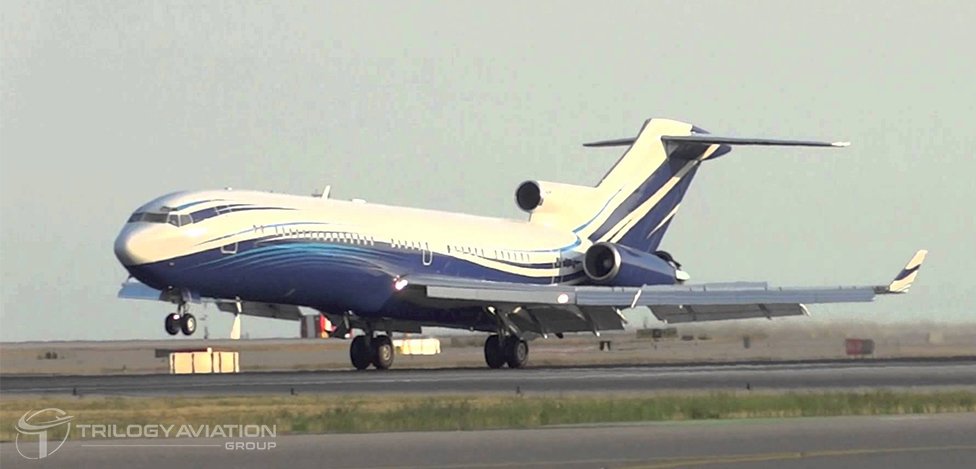
Throughout the 1960s, 70s, and 80s, the Boeing 727 became the backbone of domestic and international carriers. Most major airlines, such as Eastern Air Lines, United Airlines, Delta, and Lufthansa, operated the aircraft extensively. Its elegant design—with three engines mounted at the rear and a distinctive T-tail—helped establish it as one of the most recognizable jet airliners in aviation history.
As newer twin-engine jets entered service, many 727s were gradually retired from airline fleets. However, their durable airframes and spacious cabins made them ideal for conversion into private jets, corporate transports, and VIP aircraft.
Today, several Boeing 727s remain preserved in museums and exhibits, including those at the Aviation Pavilion, where visitors can step aboard and experience the aircraft firsthand.
Even now, a select few continue to fly in specialized roles, carrying forward the remarkable legacy of the 727.
Tri-Jet Engine Design and Advantages
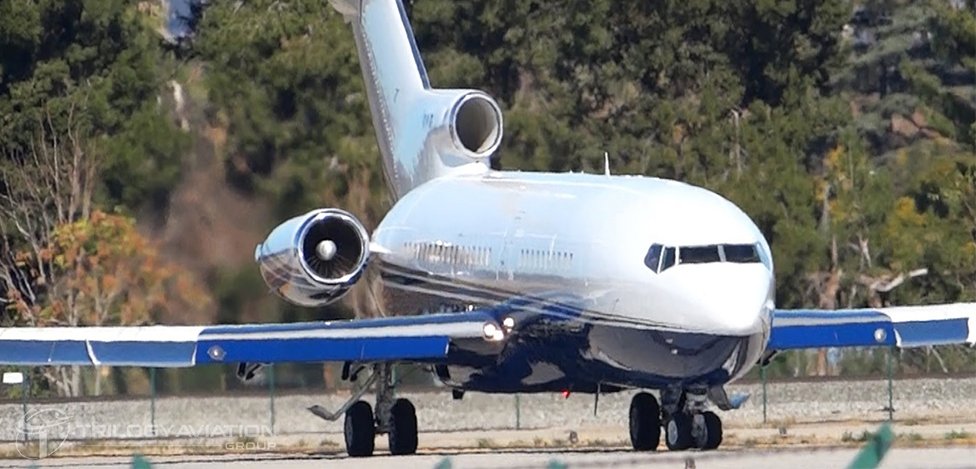
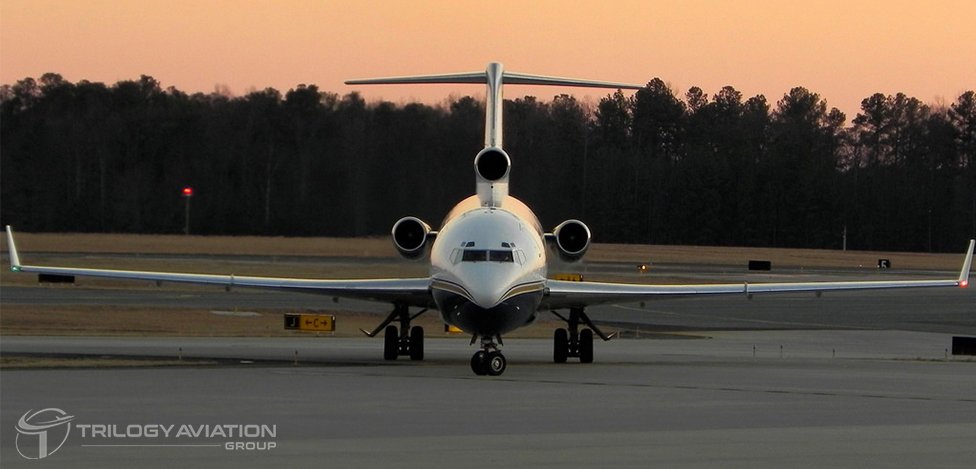
One of the Boeing 727’s most distinctive features is its tri-jet engine configuration. Equipped with three powerful Pratt & Whitney JT8D turbofan engines—two mounted on the fuselage sides and a third engine integrated into the tail through an S-duct beneath the vertical stabilizer—the aircraft was engineered for both efficiency and reliability.
This innovative design gave the 727 several advantages that remain relevant in private aviation:
- Shorter Runway Operations: The combination of its high-lift wing design, optimized takeoff performance, and the thrust of three powerful engines allowed the 727 to use shorter runways. This capability makes it suitable for accessing smaller, regional airports that many larger jets cannot.
- Balanced Power and Safety: With a third engine providing an additional layer of redundancy, the 727 offered an extra margin of reliability. Even in the event of an engine issue, the aircraft could continue operating effectively and safely.
- Operational Flexibility: The tri-jet setup delivered strong performance across varied environments, from high-altitude airports to shorter coastal strips. Additionally, the aircraft could be powered by a ground-based power supply during airport operations, minimizing fuel consumption while parked and enhancing efficiency for private operators.
For private travelers, this means greater access to unique destinations, reduced travel time, and confidence in the aircraft’s proven engineering.
Passenger Capacity and Cabin Configurations
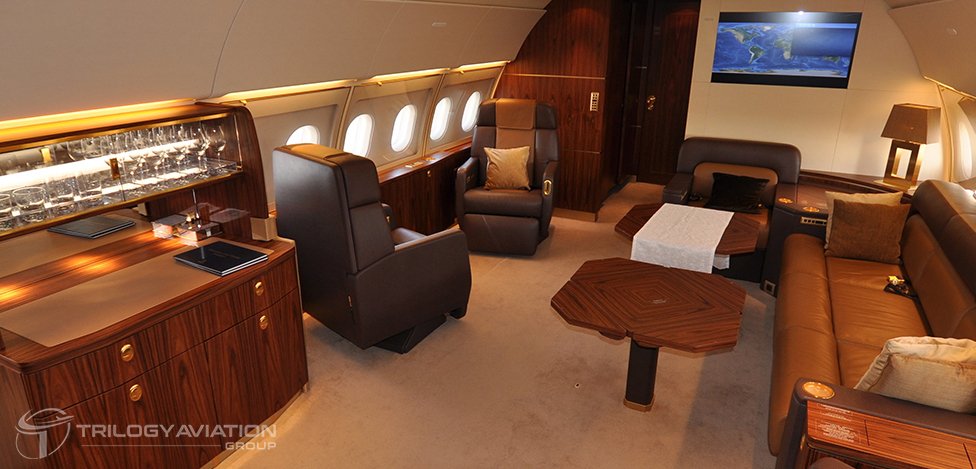
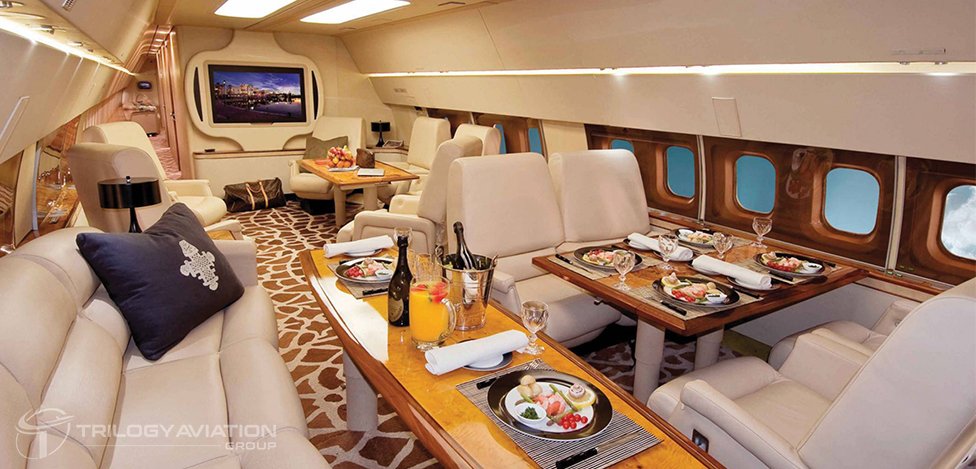
In commercial service, the Boeing 727 typically carried between 149 and 189 passengers, depending on the model. However, in a private jet configuration, the aircraft becomes a flying palace.
Private 727s often accommodate 25 to 40 passengers, with layouts that emphasize comfort, exclusivity, and personalization. The spacious cabin allows for multiple zones, such as:
- Executive seating areas with plush leather chairs and conference tables.
- Lounges for socializing, dining, or entertainment.
- Private suites with bedroom-style setups for long-haul comfort.
- Dedicated workspaces, ensuring executives can remain productive in the air.
This level of flexibility means the Boeing 727 can be tailored to meet the unique requirements of VIP groups.
Range and Performance Metrics
The Boeing 727 was designed primarily for short- to medium-range routes, but its performance profile makes it exceptionally well-suited for private operations. Depending on the variant, the 727 offers:
- Range: Approximately 1,500 to 2,700 nautical miles, depending on configuration and payload.
- Cruise Speed: Around 570 mph, ensuring timely arrivals.
- Operational Altitude: Up to 42,000 feet, making it capable of operating comfortably from high altitude hubs where thinner air can challenge less capable aircraft.
A key advantage for private operators is the aircraft’s auxiliary power unit (APU), which allows the 727 to operate independently of ground support equipment—ideal for remote airports or quick turnarounds. Its rugged landing gear and design also enable operations on shorter runways compared to many other jets in its class.
Another distinctive feature is the rear fuselage engine placement, which not only contributes to the aircraft’s signature look but also reduces cabin noise for passengers.
For private travelers, this translates into the ability to handle regional hops or medium-length international flights with ease. Routes such as New York to Los Angeles, Miami to South America, or London to the Middle East are all within reach, making the 727 a versatile choice for both business and leisure missions.